Improving the Performance of a Reduced-Order Mass-Consistent Model for Urban Environments and Complex Terrain With a Higher-Order Geometrical Representation
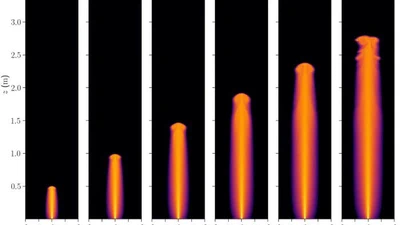
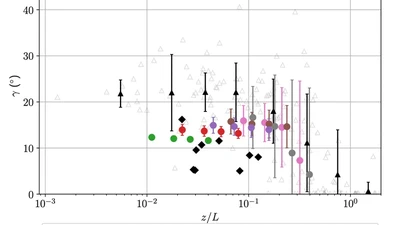
Solid structures (buildings and topography) act as obstacles and significantly influence the wind flow. Because of their importance, faithfully representing the geometry of …