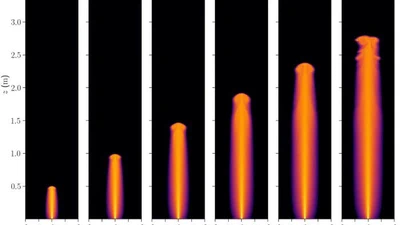
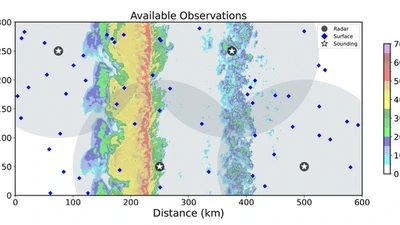
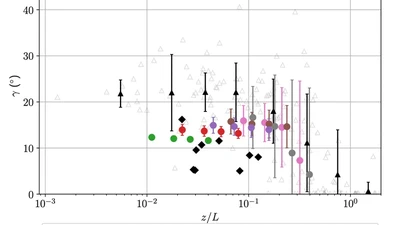
Evaluation of planetary boundary layer parameterization schemes using WoFS ensemble members and observations from TRACER
Coastal breeze circulations (bay breeze (BB), sea breeze (SB)) modulate weather conditions by advecting a maritime airmass onshore, altering air quality, and often initiating deep …