A method for generating a quasi-linear convective system suitable for observing system simulation experiments
Abstract
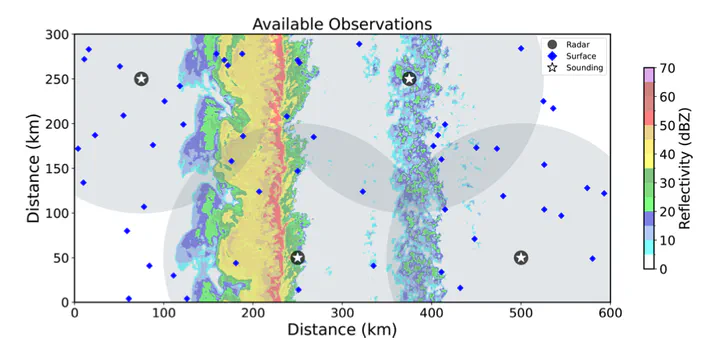
To understand the impact of different assimilated observations on convection-allowing model forecast skill, a diverse range of observing system simulation experiment (OSSE) case studies are required (different storm modes and environments). Many previous convection-allowing OSSEs predicted the evolution of an isolated supercell generated via a warm air perturbation in a horizontally homogenous environment. This study introduces a new methodology in which a quasi-linear convective system is generated in a highly sheared and modestly unstable environment. Wind, temperature, and moisture perturbations superimposed on a horizontally homogeneous environment simulate a cold front that initiates an organized storm system that spawns multiple mesovortices. Mature boundary layer turbulence is also superimposed onto the initial environment to account for typical convective-scale uncertainties.
Creating an initial forecast ensemble remains a challenge for convection-allowing OSSEs because mesoscale uncertainties are difficult to quantify and represent. The generation of the forecast ensemble is described in detail. The forecast ensemble is initialized by 24 h full-physics simulations (e.g., radiative forcing, surface friction, and microphysics). The simulations assume different surface conditions to alter surface moisture and heat fluxes and modify the effects of friction. The subsequent forecast ensemble contains robust non-Gaussian errors that persist until corrected by the data assimilation system. This purposely degraded initial forecast ensemble provides an opportunity to assess whether assimilated environmental observations can improve, e.g., the wind profile. An example OSSE suggests that a combination of radar and conventional (surface and soundings) observations are required to produce a skilled quasi-linear convective system forecast, which is consistent with real-world case studies. The OSSE framework introduced in this study will be used to understand the impact of assimilated environmental observations on forecast skill.
Creating an initial forecast ensemble remains a challenge for convection-allowing OSSEs because mesoscale uncertainties are difficult to quantify and represent. The generation of the forecast ensemble is described in detail. The forecast ensemble is initialized by 24 h full-physics simulations (e.g., radiative forcing, surface friction, and microphysics). The simulations assume different surface conditions to alter surface moisture and heat fluxes and modify the effects of friction. The subsequent forecast ensemble contains robust non-Gaussian errors that persist until corrected by the data assimilation system. This purposely degraded initial forecast ensemble provides an opportunity to assess whether assimilated environmental observations can improve, e.g., the wind profile. An example OSSE suggests that a combination of radar and conventional (surface and soundings) observations are required to produce a skilled quasi-linear convective system forecast, which is consistent with real-world case studies. The OSSE framework introduced in this study will be used to understand the impact of assimilated environmental observations on forecast skill.
Type
Publication
Geoscientific Model Development, 16(6), 1779–1799